Building the Beloved Character, Part 3
/What can two chairs have to do with building a fictional character?
Read MoreInternational Award-Winning Author
What can two chairs have to do with building a fictional character?
Read MoreThat the woman was Dutch seemed at first to be an obstacle, but then I realized it was in fact an unexpected but perfect solution.
Read MoreHow history repeats in the comparison between Thomas Cromwell and Thomas Wentworth
Read MoreRecently when I opened my Facebook account, an unexpected memory awaited. It was this picture, taken in 2001 to promote a new book that was a long time in coming, and a source of pride for these three co-authors, Terry Nosho, David G. Gordon, and yeah, that’s me in the middle.

Time has altered our faces, but not the joy and passion for that book...that book...
One day, about a year and a half before this picture was taken, a young man in jeans, mud boots and a rumpled shirt came into my office. He plopped down on our worktable a most magnificent thing: a scrapbook of enormous proportions, with a kelly-green cover nearly the size of my refrigerator door, and spiral-bound pages stacking three inches high.
“My grandfather’s an oyster grower. He’s been keeping this thing for years, sticking this and that in it,” the man said. “Newspaper articles, pictures, restaurant menus, napkins, all sorts of things. He wants to know if you can do something with it. Anyway, it’s yours now.”
Well, not mine, exactly, but the grant program for which I worked, housed with the School of Fisheries and Oceanography at the University of Washington. Our offices were repurposed student housing, a stone’s throw from Montlake cut between Lake Washington and Lake Union where the University’s famed rowing team practiced.
Our program’s educational and research support for the oyster industry, led by Terry Nosho, was well regarded as perhaps the only positive attention paid by anyone to the health and survival of oyster farming.
The whump of the scrapbook on the table was enough to draw my team from their desks: David first, being most curious; then Robyn, the graphic designer; then Susan, the webmaster. We turned the first page. I can’t speak for the rest of them but I was immediately spellbound. Those pages contained a world: not just the history of Washington state’s oyster resource, but of the farming and consumption of oysters, of their culture, and the culture of the families that made a living from them, can labels, matchbook covers, cartoons, and so much more. What could we do with such treasure?
And to me it truly was treasure, as I considered the thoughts and hands and eyes of the person who had compiled this book faithfully and consistently over the decades, the stories this book told and the stories that were never told.
On David’s thoughtful lead—he was already a published author several times over— we perused that scrapbook for different threads that we could weave into a historical look at the world of Washington oysters, complete with recipes and gorgeous photography of Washington’s iconic coast. The result was Heaven on the Half Shell, the Story of the Pacific Northwest’s Love Affair with the Oyster.
It was a powerful experience. It became an opportunity to capture its essence in an idea, grow the idea into a viable project, and then produce a book that not only encapsulates time, but also stands the test of it.
A new door had opened. The love of history and adventure ran in my veins—my favorite book as a child was Robinson Crusoe—and now I learned how to research things, what to look for, how to turn history and discovery into story, and turn story into a touchable, colorful, ink-scented book for anyone to enjoy.
It wouldn’t be long before my own history came knocking; before passion, experience and heritage merged, and I had to find out. I had to know. What happened in the lives of my ancestors? Did they actually live in...castles? Did they suffer? Did they fight? Did they rise? The truth eludes me. The facts are veiled or nonexistent. There is conjecture. Mystery. Hearsay and propaganda.
I search through the documents, books and biographies available, and fill in the blanks as I best I can. It’s a little like prying open an oyster shell, but not as sharp. And four books later I begin again, wondering still why I love it so, this thing with history?
Last month at the Amelia Island Book Festival in Florida, I received another gift: the opportunity to chat with New York Times best-selling author Margo Lee Shetterly. If you do not recognize the name, you’ll recognize her book: Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space Race.
Not historical fiction, but classified as narrative non-fiction, her book required a great deal of research, and when I told her that the former journalist in me greatly admired the work she had done to create that book, we connected on the love of research.
She lamented that several of the people she’d hoped to interview for her next book had already passed away. The same was true when we were researching the oyster book. People had either passed away or were too distrusting of “government” to speak with us. I replied that, writing about the 17th century meant all my people had passed away, but fortunately in those days they wrote letters. What will happen, we wondered, when such detailed written documentation of emotion and experience is lost?
I believe we will find it still, in blog posts and videos, in personal journals, in the work of historians, archaeologists and anthropologists who will always dig for the truth.
If history infiltrates other thoughts, usurps other interests, occupies every bookshelf, makes you the geek at parties, and so on—then it is both gift and responsibility. The study of history becomes a joyful treasure hunt that not everyone seeks or understands, but the responsibility is to give attention and meaning to a particular time and people who lived it.
With the help of inspiration, you get to share these discoveries in a way that engages people so that they get those same messages. Carry on!

Happy after my first novel won gold at the Florida Writers Association.
Malahide Castle is famous for surviving through tumultuous and violent centuries, and provides a fascinating glimpse into life in an ancient fortress, and the enduring spirit of the family that lived there.
Read MoreIn his brightest hour, as chief advisor to King Charles I of England, he was loved by some and deeply hated by others. And yet, one is likely to feel respect for him, if not true admiration.
Read MoreAttention to detail and accuracy is what marks the difference between the hobbyist and the professional. And some of us actually enjoy the research.
Read MoreJust before the turn of the 17th century in 1593, Thomas Wentworth was born in London, into fortune, property and prestige. But he sought more than anything what he did not have: a royal title. An earldom. It would come at the greatest cost.
Read MoreYou can try to ignore “that voice” until you’re blue in the face but that's not enough: the name of the game is to get it on your side…to make it an ally. You can learn to use its’ energy to your advantage.
Read MoreIt remains one of my greatest treasures. And, it cemented my love for historical fiction. My mother knew that, but I don’t think she took credit where it was certainly due. Since then I have never been bored.
Read MoreTo walk along the road in front of several quaint thatched cottages, you might believe you are in an ancient neighborhood, and perhaps wish that you were.
Read MoreThis is a beautiful and dramatic cave that has been explored extensively since it was discovered in 1833, when a Michael Condon accidently dropped his crowbar into a crevice while quarrying for stone.
Read MoreMallow Castle has large mullioned windows, loopholes for muskets, and fireplaces in each room that stir the imagination. Who once warmed their hands or dried their clothes there, and what did they think about?
Read MoreOn a dark June night of 1631, three ships arrived carrying Algerian pirates who stormed ashore, killing two of the town’s residents and capturing 107 men, women and children.
Read More
Part 11 in a series featuring sites I visited in Ireland while researching my second novel, The Prince of Glencurragh. See previous posts listed at the end.Just west of Castletownshend and less than four miles from Skibbereen, there once was a ring fort high on a hill. All but gone now, the place still bears the name, Liss Ard, meaning “high fort.” Turning off the main road, instead of discovering a ruin you’ll come to an attractive high-end resort near the tranquil waters of Lough Abisdealy.
Here, along its lush banks, I found the very tree I needed for an exciting scene in The Prince of Glencurragh. It is here that protagonist Faolán Burke sets his trap for the bad guy who stalks him, Geoffrey Eames. Eames ends up tied to the tree, his feet at the water’s edge, and is left to his own devices to get himself free. Appropriate, perhaps, because by at least one source Lough Abisdealy means “lake of the monster.”


On a map, the shape of Abisdealy looks to me like a giant sperm whale with its tail flipped up. While the lake is a favorite spot for some who fish for pike or carp, it has also produced sightings of another kind of monster, the conger or horse eel—giant eels in the likeness of the Loch Ness monster, as described in another location:
When the normally gushing waters linking lakes and rivers became reduced to a pathetic drizzle a large horse-eel was discovered lodged beneath a bridge by Ballynahinch Castle. The beast was described as thirty feet long and “as thick as a horse.” A carpenter was assigned to produce a spear capable of slaying the great creature but before the plan could be carried through rains arrived to wash the fortunate beast free. ~ Dale Drinnon, Frontiers of Zoology
And in 1914 at Lough Abisdealy, author Edith Somerville reported sighting “a long black creature propelling itself rapidly across the lake. Its flat head, on a long neck, was held high, two great loops of its length buckled in and out of the water as it progressed.”
I saw no snakes, eels or monsters when I visited the lake, but what I did see was a visual feast of trees, their forms twisted, curved and swayed as if they were dancing.





If you have an extra €7,500,000 handy you can pick up the estate for your very own. The real estate sales listing describes the “truly remarkable” 163-acre residential estate as a pleasure complex with Victorian mansion (6 bedrooms), Mews House (9 bedrooms) and Lake Lodge (10 bedrooms), plus tennis court, private 40-acre lake, and the Irish Sky Garden designed by artist James Turrell where you might “contemplate the ever-changing sky design.”
While it is not from the 17th century when my novel is set, the location does have some history to it:
“The Mansion house was built by the O'Donovan Chieftain of the O'Donovan Clan circa 1850 and a summer house, a moderately large house, was added to the estate circa 1870. This Summer House now referred to as the Lake Lodge.”
From the lake, the characters in The Prince... are just a few more miles from their destination, Rathmore Castle at Baltimore, and an important meeting with the Earl of Barrymore.

The Prince of Glencurragh is available in ebook, soft cover and hard cover from online booksellers.
OR, try this universal link for your favorite ebook retailer: books2read.com
Learn more and sign up for updates via my newsletter at nancyblanton.com
Part 9 in a series featuring sites I visited in Ireland while researching my second novel, The Prince of Glencurragh. See previous posts listed at the end. I first discovered Coppinger’s Court as a notation on a West Cork tour map. I was seeking a route that my characters in The Prince of Glencurragh would travel from Timoleague to Clonakilty and west along the coast to Baltimore. I wondered if it might become a stopping place along their way, but instead the manor house was so dramatic it inspired another scene altogether.
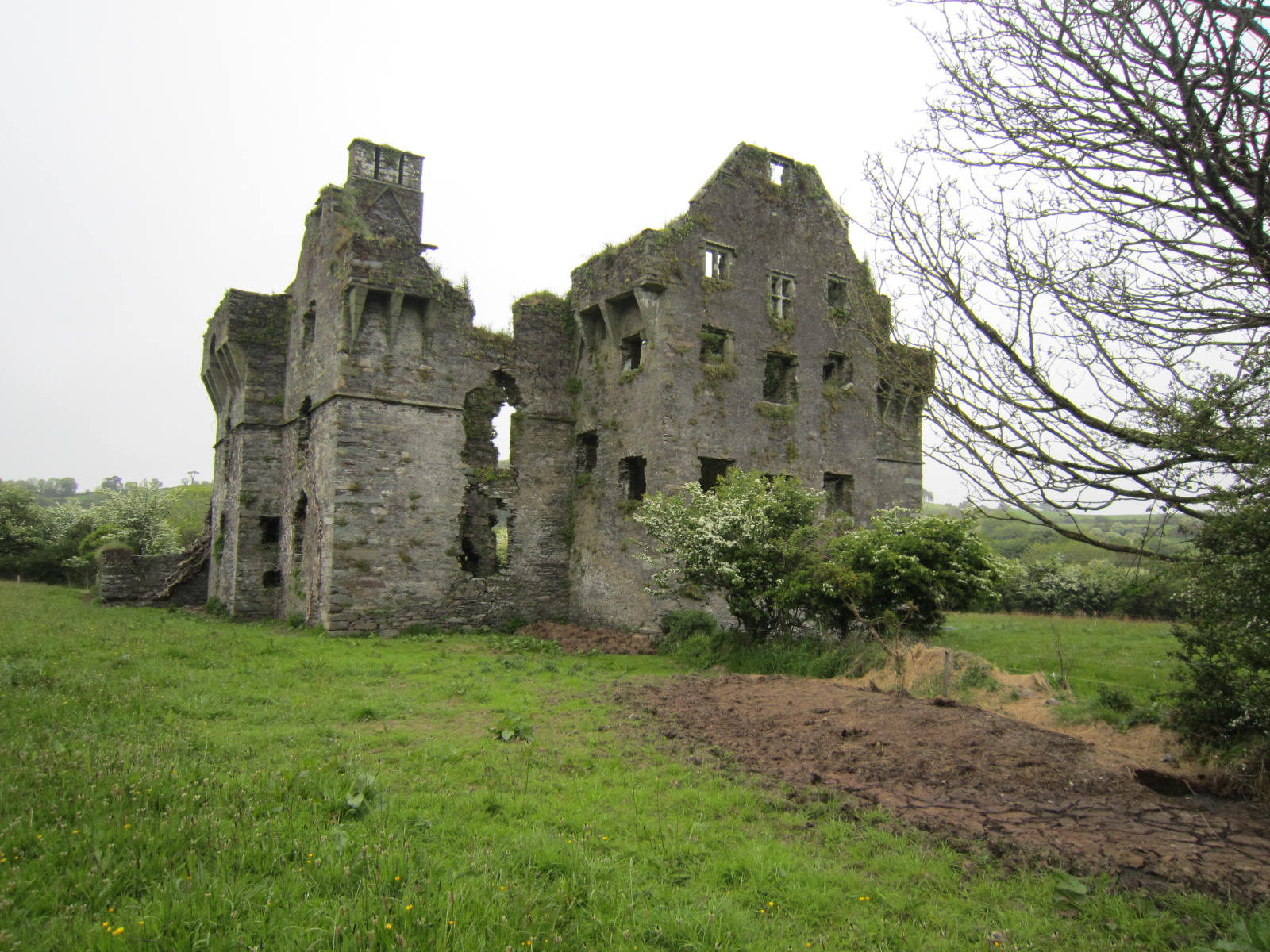 Coppinger’s Court, also known as Ballyvireen, is located along the Glandore road about two miles west of Rosscarbery. Described as a fortified manor house in the Elizabethan style, the structure has three wings off of a central court, creating nine gables, and each exterior wall has large mullioned windows that would have ensured good natural light.
Coppinger’s Court, also known as Ballyvireen, is located along the Glandore road about two miles west of Rosscarbery. Described as a fortified manor house in the Elizabethan style, the structure has three wings off of a central court, creating nine gables, and each exterior wall has large mullioned windows that would have ensured good natural light.
Considered a place of opulence in its day, the house was said to have been “the finest house ever built in West Cork,” and is credited with having “a chimney for every month, a door for every week, and a window for every day of the year.”
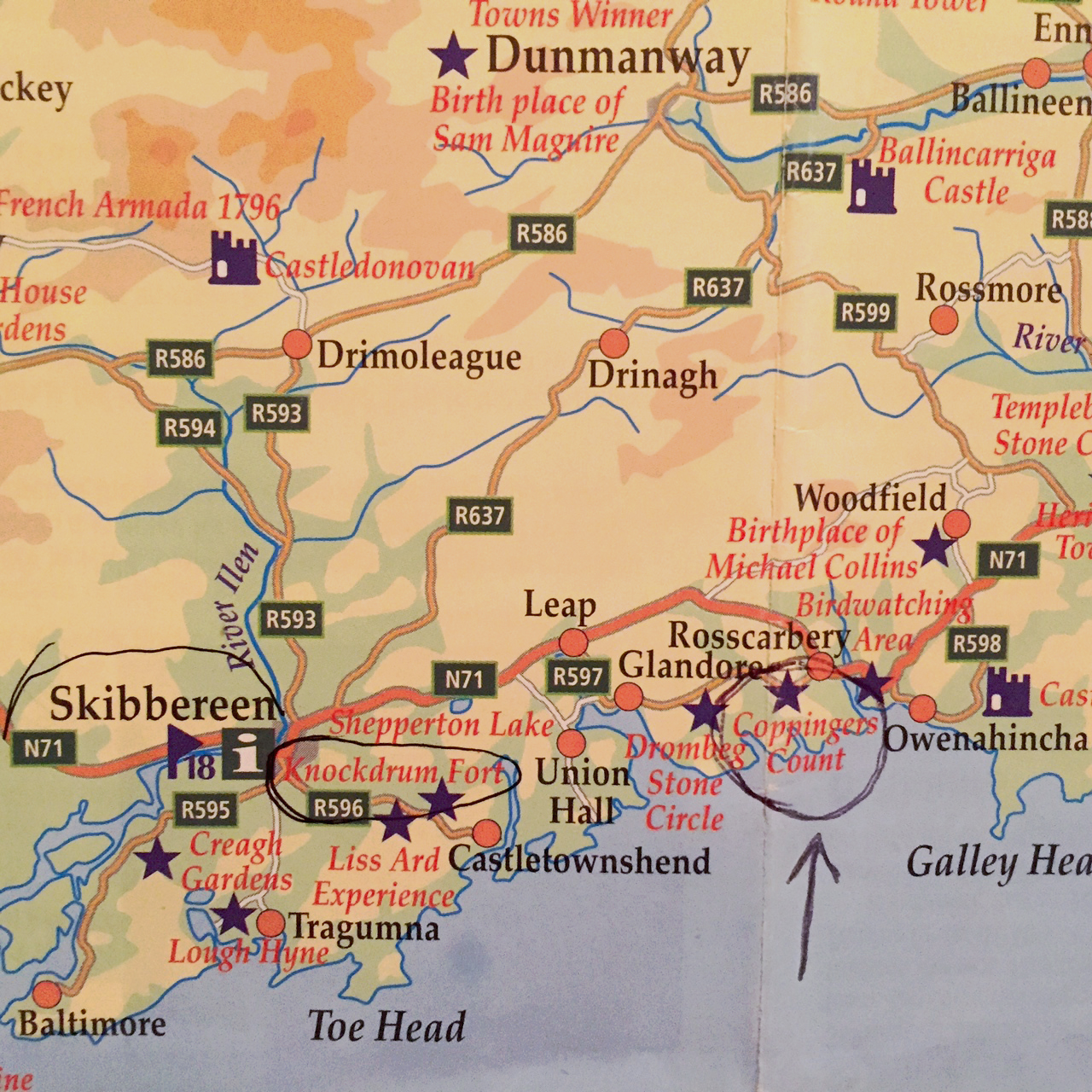 With a description like that, I had to see it. And I already knew it would become the model for the fictitious Rathmore House, the seaside home of the Earl of Barrymore located near the town of Baltimore.
With a description like that, I had to see it. And I already knew it would become the model for the fictitious Rathmore House, the seaside home of the Earl of Barrymore located near the town of Baltimore.
In The Prince of Glencurragh, Faolán Burke, his abducted/intended bride, and accomplices are rushing across Ireland’s south coast toward Baltimore. There they must meet the Earl of Barrymore who has promised to negotiate the marriage settlement. The story takes place in 1634, just three years after the town of Baltimore has been devastated by an attack and raid by Algerian pirates.
This attack was a real and violent event. Most of the town’s residents were abducted, a small number of them were ransomed, and the rest were killed, sold or used as slaves. The few survivors moved inland to Skibbereen for safety. I placed the Earl of Barrymore’s house, Rathmore, at a cove between the two settlements.
 And I soon discovered a close and perhaps sinister connection between Coppinger’s Court and the town of Baltimore, centered on the builder of the great house, Sir Walter Coppinger. Sir Walter took pride in his Viking bloodline, and descended from a mercantile family well known in Cork for centuries:
And I soon discovered a close and perhaps sinister connection between Coppinger’s Court and the town of Baltimore, centered on the builder of the great house, Sir Walter Coppinger. Sir Walter took pride in his Viking bloodline, and descended from a mercantile family well known in Cork for centuries:
“In 1319 Stephen Coppinger was mayor of the city, and several of his descendants held this position as well as becoming bailiffs and sheriffs of Cork. The Coppingers remained Roman Catholic and could therefore only afford to build a relatively modest residence at Glenville, of two storeys and five bays fronted by a semi-circular courtyard with a gate at either end.” ~ The Irish Aesthete
Sir Walter, however, was far from modest. He was a businessman, lawyer, landowner, and moneylender, who acquired many of his properties from borrowers who defaulted on their loans. Several sources support his reputation for ruthlessness, and perhaps unscrupulousness.
“Sir Walter Coppinger is remembered, probably wrongly, as an awful despot who lorded it over the district, hanging anyone who disagreed with him from a gallows on a gable end of the Court.” ~ Abandoned Ireland
Sir Walter wished to own Baltimore for its castle and properties, and lucrative pilchard industry. He was involved in legal battles for ownership, but in 1610 he and other claimants agreed to lease the town to English settlers for 21 years. By the end of the lease, Coppinger had brought a case before the king’s Star Chamber, claiming the town as his own and asking to evict the English settlers. But he grew frustrated when the chamber members were reluctant to decide the case, and reluctant to evict prosperous families who had made improvements to the properties. And then came the pirates.
“There is no concrete evidence that Coppinger had any role in organising the Algerine raid of 1631. But it conveniently removed the only obstacle to his total control of Baltimore.” ~ Des Ekin, The Stolen Village
If he was responsible, it seems Karma won in the end. Coppinger was not to benefit from his long-coveted Baltimore. The town’s vast annual pilchard run suddenly disappeared, and by 1636 he had leased out his new castle and village. Sir Walter died in 1639. Then came the great Irish rebellion of 1641. Coppinger’s Court was ransacked and burned, and then confiscated by Oliver Cromwell in 1644. By 1690 after years of disuse, the great house was on its way to becoming another beautiful ruin.

Thanks to The Irish Aesthete, Exploring West Cork by Jack Roberts, The Stolen Village by Des Ekin, abandonedireland.com,
 An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
The Prince of Glencurragh is available in ebook, soft cover and hard cover from online booksellers.
Learn more and sign up for my newsletter at nancyblanton.com
https://books2read.com/u/4N1Rj6
http://www.amazon.com/Prince-Glencurragh-Novel-Ireland-ebook/dp/B01GQPYQDY/
Part 8 in a series featuring sites I visited in Ireland while researching my second novel, The Prince of Glencurragh. See previous posts listed at the end. Sometimes, though sand and water wash away the past, research and imagination still can resurrect it.
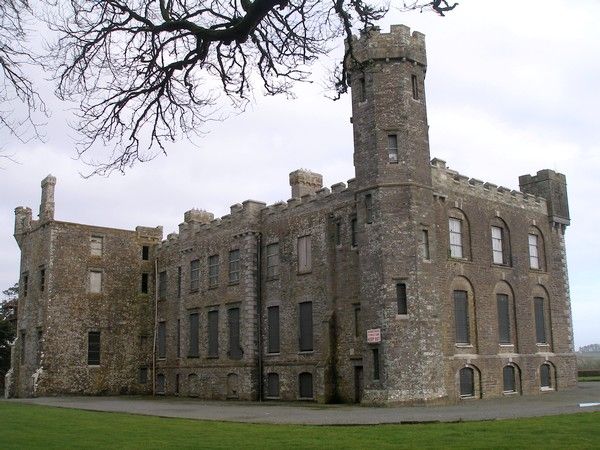

From Timoleague, Clonakilty is nearly a straight shot west along the R600. Heading south from there are rolling hills, green bluffs and marshy expanses leading toward Dunnycove Bay. On most driving and tour maps you’ll see a notation for Castlefreke.
Built by Randall Oge Barry in the 15th century, the fort was lost to the English after the Battle of Kinsale, was besieged and later burned during the Rebellion of 1641. A tower house was built on the site in 1780, which was remodeled in 1820, burned down in 1910, and at the time of my visit it was being remodeled as an event venue. However we did not visit Castlefreke itself, because it was not my destination. Instead, I wished to see Rathbarry Castle, the Red Strand, and just a little farther west, Coppinger’s Court.

Featuring characters from the Barry family in The Prince of Glencurragh, I sought locations where they might have met or slept. I was to find little remaining of the castle, but enough to stir my imagination, and even more so, the illuminate larger forces that had been in play in the region.

Thanks to my friends Eddie and Teresa, who introduced me to their friend Pat Hogan, I was able to visit and learn much about Rathbarry, and it became a landmark in the book, near the cottage of the mysterious healer Pol-Liam.
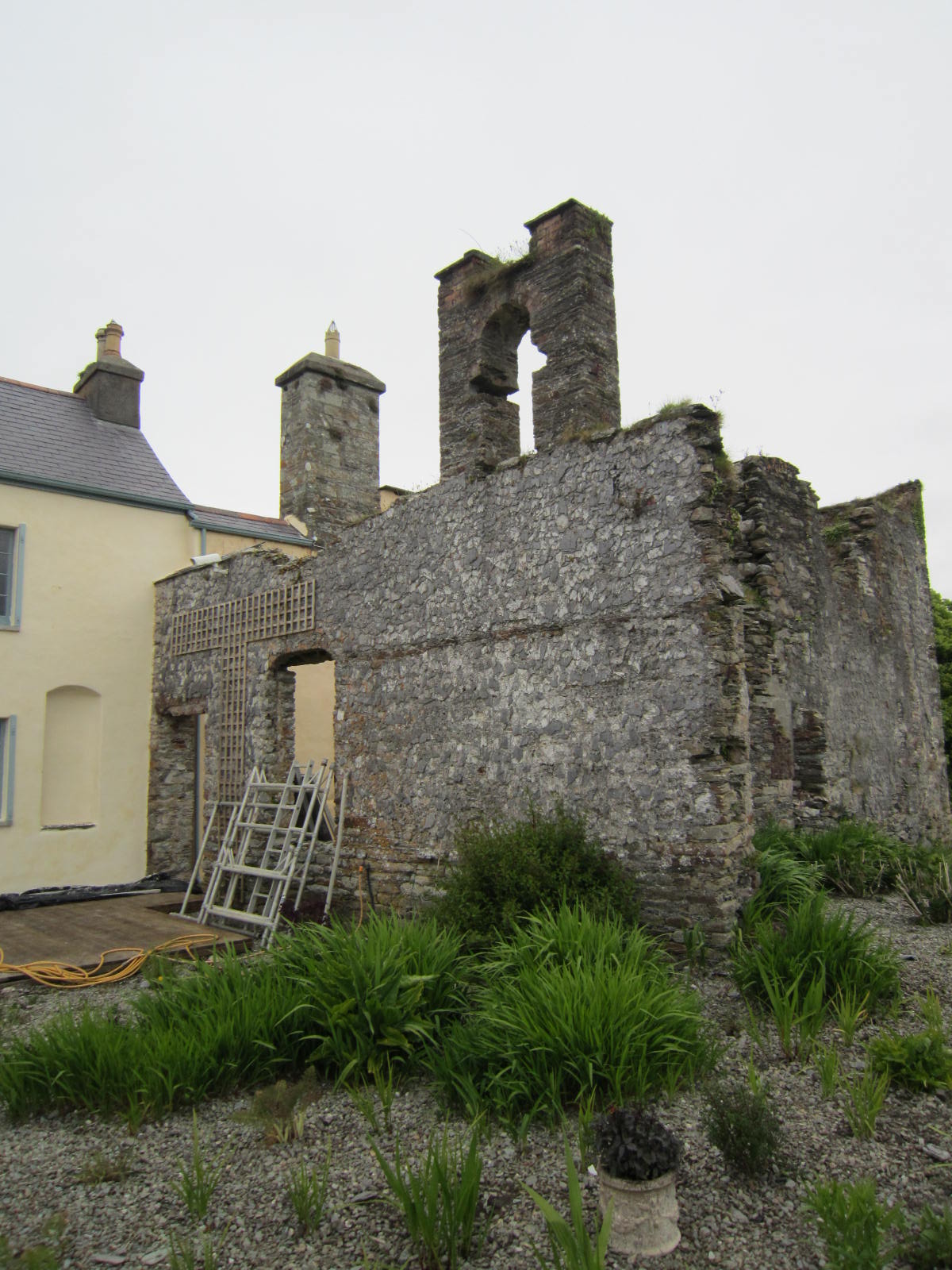
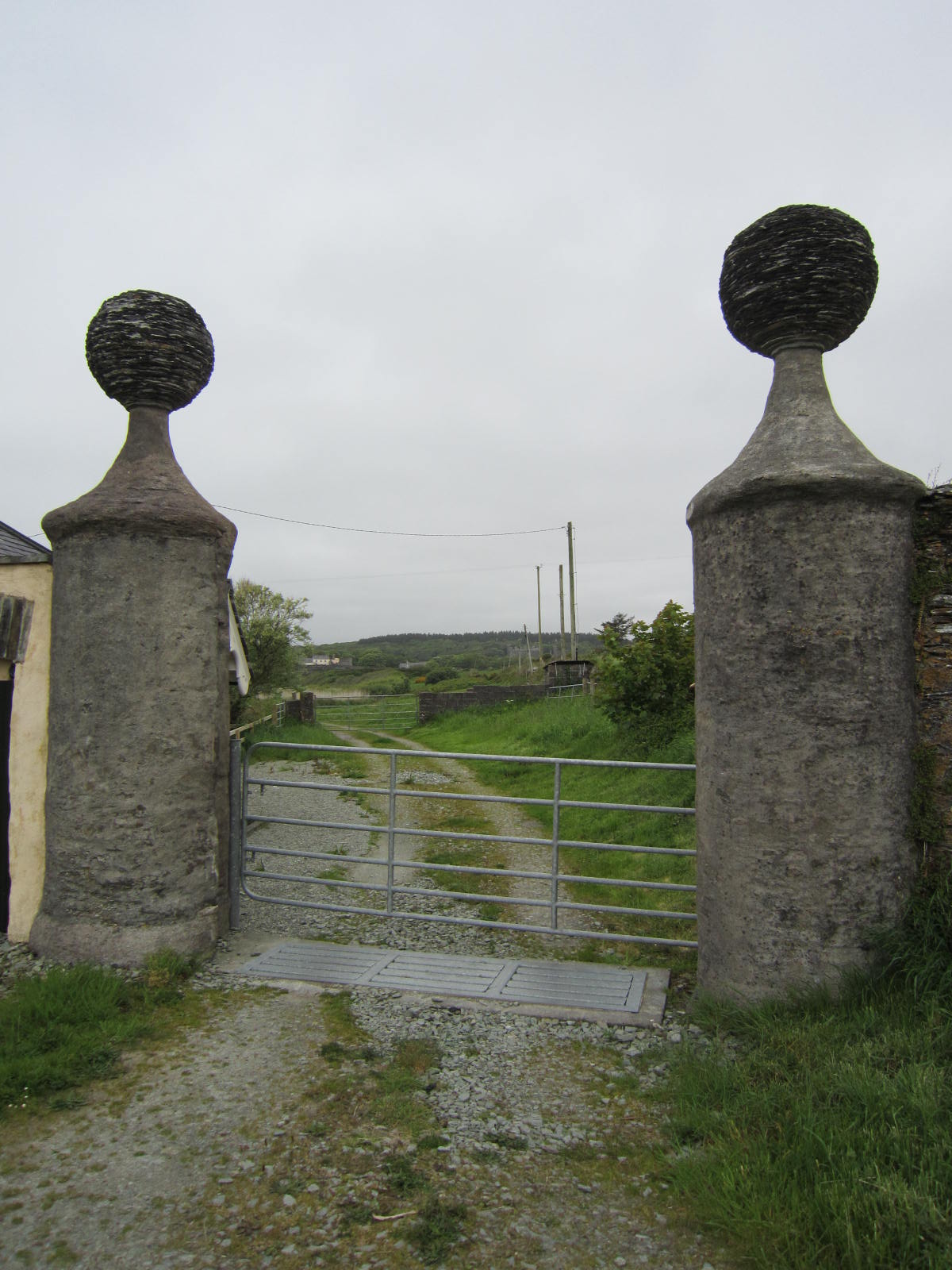
 The castle Rathbarry existed on the site of what is now Castlefreke, bearing the family name of Freke for the current owners. Far out on the roadway, the gateposts marking the entrance to the castle grounds with their large spherical tops were said to be true remnants of the 17th century. Just one wall of the ancient stables and carriage house remained, and a new stable house had been built within it remodeled as a private residence. We were treated to a peek inside this structure to get a feel for what home life was like there.
The castle Rathbarry existed on the site of what is now Castlefreke, bearing the family name of Freke for the current owners. Far out on the roadway, the gateposts marking the entrance to the castle grounds with their large spherical tops were said to be true remnants of the 17th century. Just one wall of the ancient stables and carriage house remained, and a new stable house had been built within it remodeled as a private residence. We were treated to a peek inside this structure to get a feel for what home life was like there.
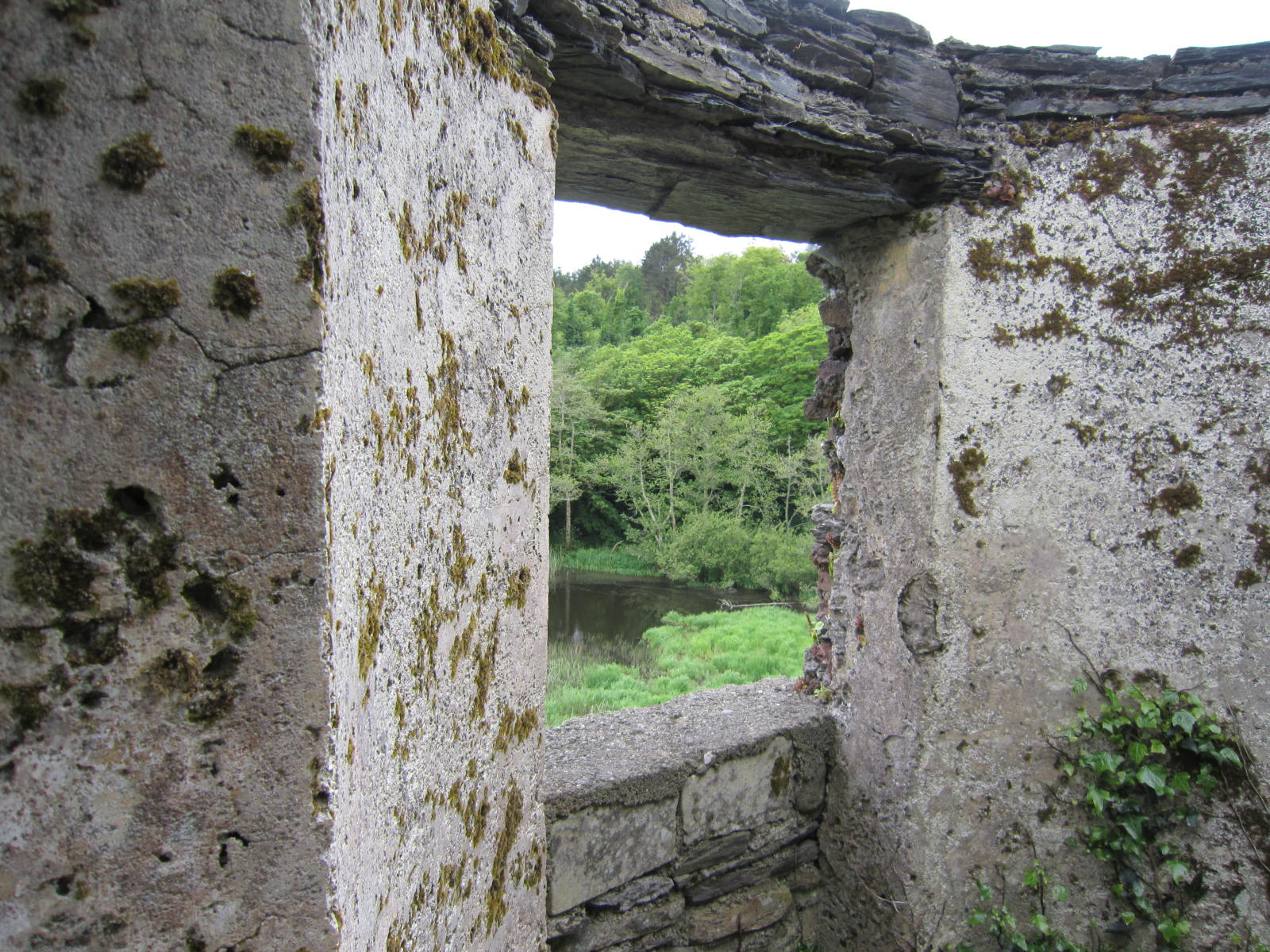 From the upper wall of the ruin, crumbling stone stairs led down to an ancient watergate, a stone passage leading directly from the castle to the water, where boats would have come to deliver food and supplies. But, except for a small, enclosed pond, there was no water. From the top of the steps I could see the bay, maybe half a mile distant. How, I wondered, could the castle have been served from such a distance?
From the upper wall of the ruin, crumbling stone stairs led down to an ancient watergate, a stone passage leading directly from the castle to the water, where boats would have come to deliver food and supplies. But, except for a small, enclosed pond, there was no water. From the top of the steps I could see the bay, maybe half a mile distant. How, I wondered, could the castle have been served from such a distance?
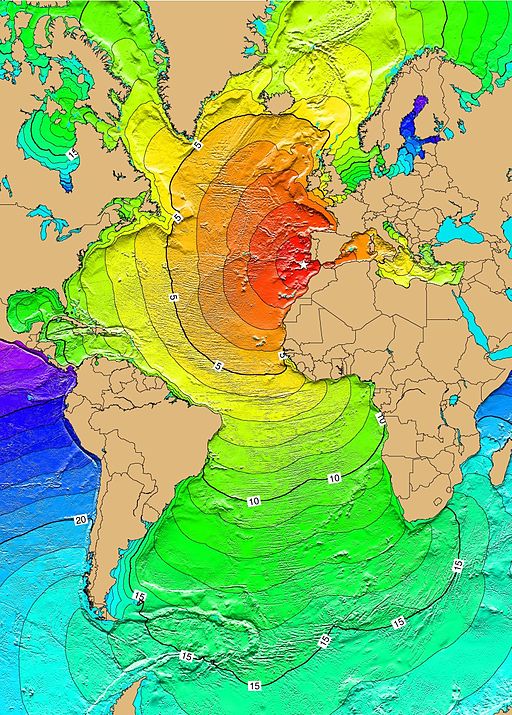
As Mr. Hogan reminded me, the landscape had changed dramatically since the 17th century, and events at the global level could have affected Ireland’s coastlines. In fact, in 1755 the Great Lisbon Earthquake and tsunami are believed to have done so. Considered one of the deadliest earthquakes in history, it is estimated to have hit the 8.5 to 9.0 range on today’s scale of magnitude, killed thousands of people and nearly devastated Lisbon. The tsunami’s impact was far-reaching.
“Tsunamis as tall as 20 metres (66 ft) swept the coast of North Africa, and struck Martinique and Barbados across the Atlantic. A three-metre (ten-foot) tsunami hit Cornwall on the southern English coast. Galway, on the west coast of Ireland, was also hit, resulting in partial destruction of the "Spanish Arch" section of the city wall. At Kinsale, several vessels were whirled round in the harbor, and water poured into the marketplace.” ~ Charles Lyell, Principles of Geology, 1830
 Gigantic waves were reported as well in the West Indies and Brazil. Could these environmental events have shifted sands and reshaped Ireland’s coastline? Undoubtedly.
Gigantic waves were reported as well in the West Indies and Brazil. Could these environmental events have shifted sands and reshaped Ireland’s coastline? Undoubtedly.
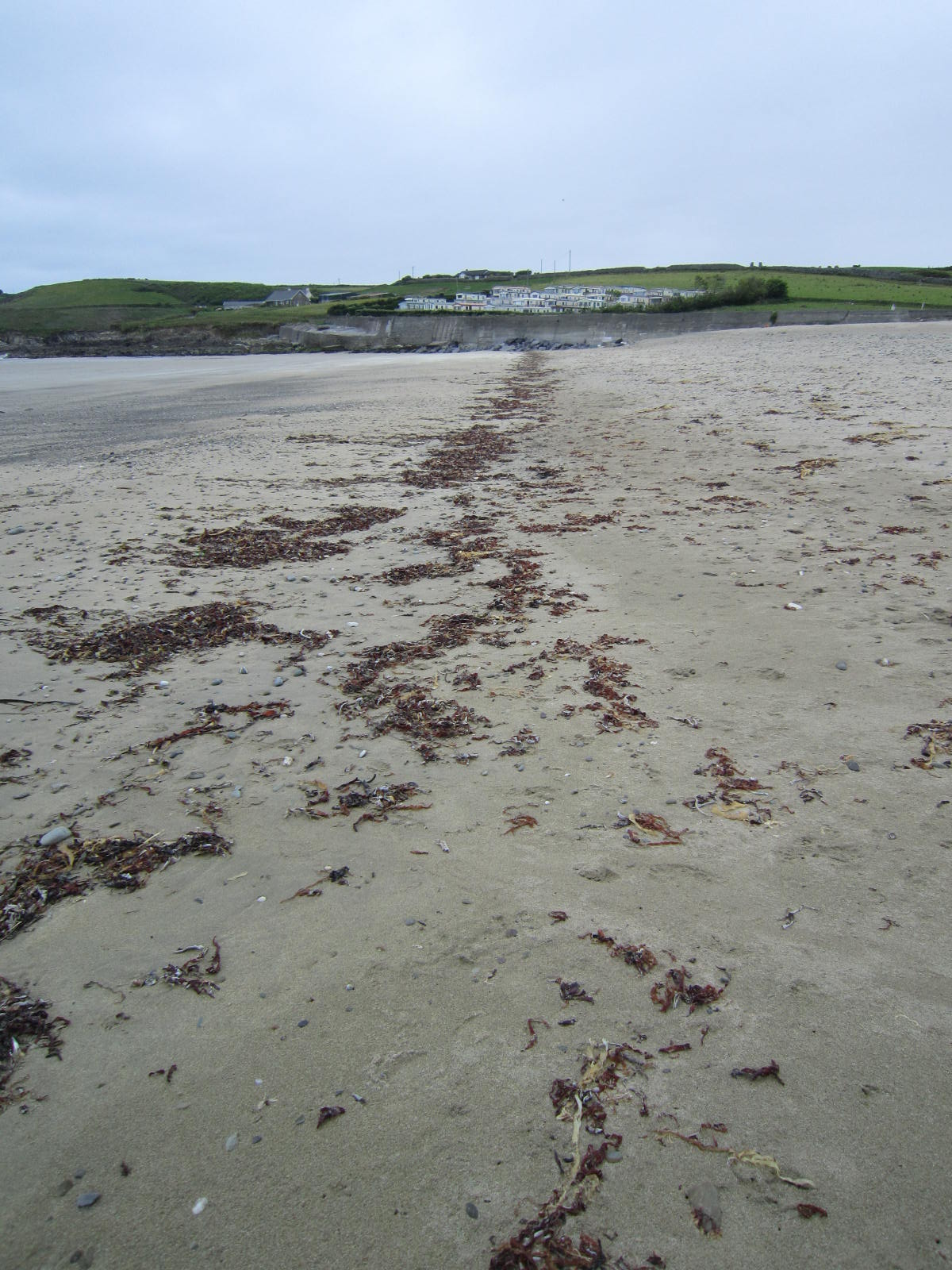
Almost within view of Rathbarry was another site I wished to visit: the Red Strand. Also likely to have been altered by the tsunami, this sandy beach was called “red” because the sand contained fossilized sea creatures or “calcareous matter,” which was believed to have a healing effect and also promote fertility. As late as the 19th century the sand was being collected for use in fertilizing crops some 16 miles away.
The only red I saw during my visit was in the clumps of seaweed washed ashore; still, the strand fascinates, bounded on one side by stones, and on the other by bluffs and stream. The strand and the story behind it served my imagination for a deadly scene in the book.
Next time: Coppinger’s Court.
Part 1 - Kanturk Castle
Part 2 - Rock of Cashel
Part 3 - Barryscourt
Part 4 - Ormonde Castle
Part 5 - Lismore Castle
 An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
The Prince of Glencurragh is available in ebook, soft cover and hard cover from online booksellers.
https://books2read.com/u/4N1Rj6
http://www.amazon.com/Prince-Glencurragh-Novel-Ireland-ebook/dp/B01GQPYQDY/
Part 7 in a series featuring sites I visited in Ireland while researching my second novel, The Prince of Glencurragh. See previous post links below.
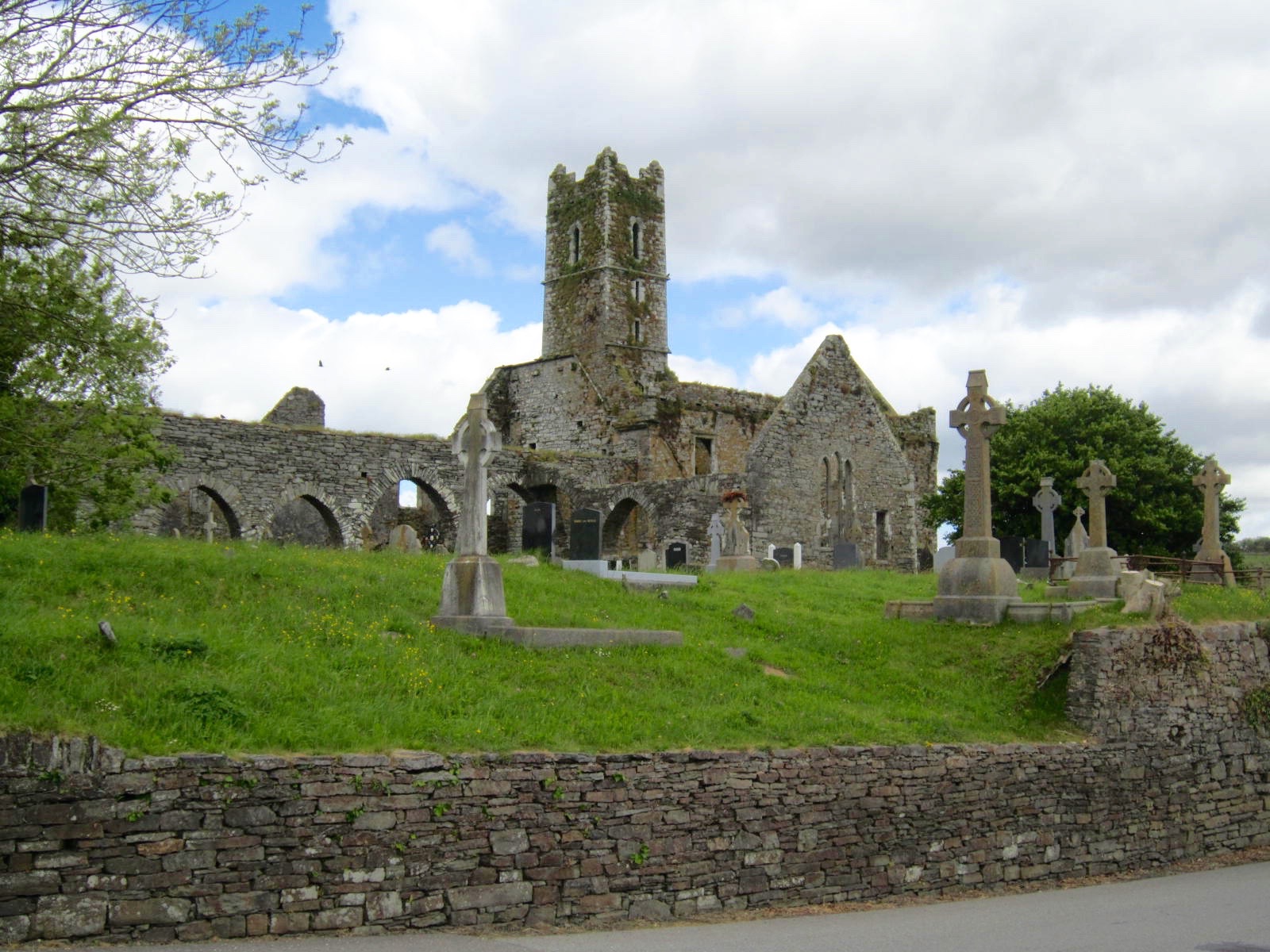 Driving south from Bandon on R602, you will arrive at the town of Timoleague in about 20 minutes, and see immediately the great landmark of Timoleague Friary. For the Prince of Glencurragh, traveling on horseback, at night and over rugged terrain, it would have taken at least three hours to reach this first stop on Faolán Burke’s path to destiny.
Driving south from Bandon on R602, you will arrive at the town of Timoleague in about 20 minutes, and see immediately the great landmark of Timoleague Friary. For the Prince of Glencurragh, traveling on horseback, at night and over rugged terrain, it would have taken at least three hours to reach this first stop on Faolán Burke’s path to destiny.
In the 17th century, local parishes were required to maintain their roads, especially in market towns. In 1634, a new act of Parliament allowed for a tax levy to cover the costs. But it would be decades before Ireland’s road systems were noted for improvements. A Scotsman traveling through Ireland in winter around 1619-1620 described his horse as “sinking to his girth” on boggy roads, his saddles and saddlebags destroyed.
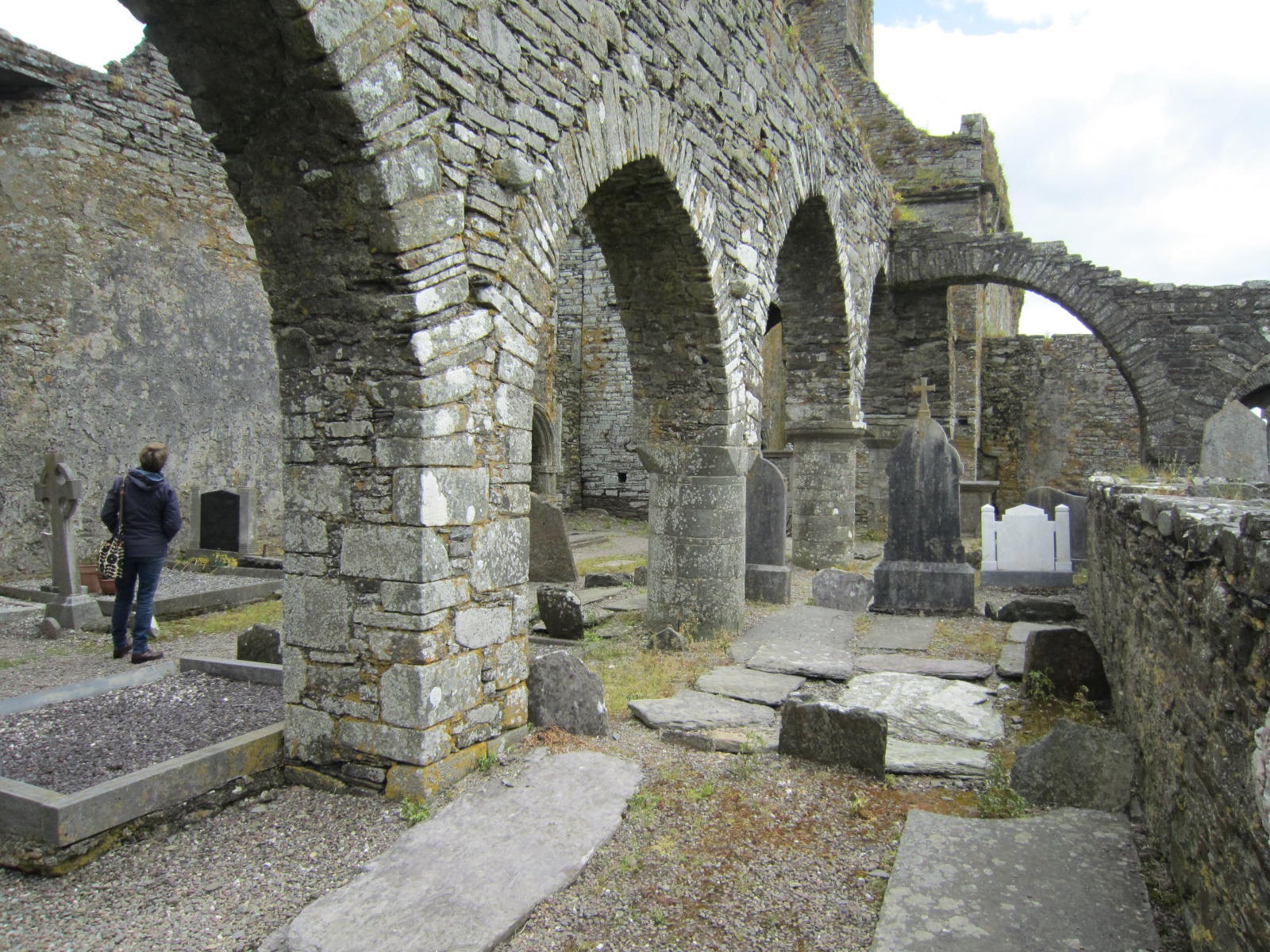 Timoleague Franciscan friary would have provided a most welcome shelter to travelers, even it its ruined state. It remains a massive and impressive structure, the walls of the various rooms still intact so that you can recognize the floor plan and how each room was used. The roof is long gone, and some sources say that parts of the structure were carted away for use in other buildings.
Timoleague Franciscan friary would have provided a most welcome shelter to travelers, even it its ruined state. It remains a massive and impressive structure, the walls of the various rooms still intact so that you can recognize the floor plan and how each room was used. The roof is long gone, and some sources say that parts of the structure were carted away for use in other buildings.
 From the mullioned window in the chorus, one would be hard-pressed to find a view more peaceful and contemplative. This is the spot where my heroine, Vivienne, considers her circumstances, having been abducted by three strange men, however benevolent they might have seemed. It’s the place where narrator Aengus recalls a treasured time with his father. And it is where he and Vivienne first realize a common bond.
From the mullioned window in the chorus, one would be hard-pressed to find a view more peaceful and contemplative. This is the spot where my heroine, Vivienne, considers her circumstances, having been abducted by three strange men, however benevolent they might have seemed. It’s the place where narrator Aengus recalls a treasured time with his father. And it is where he and Vivienne first realize a common bond.
Scenes in the book came alive for me as I entered each room and walked the same paths of monks and soldiers, and imagined conversations echoed in my mind.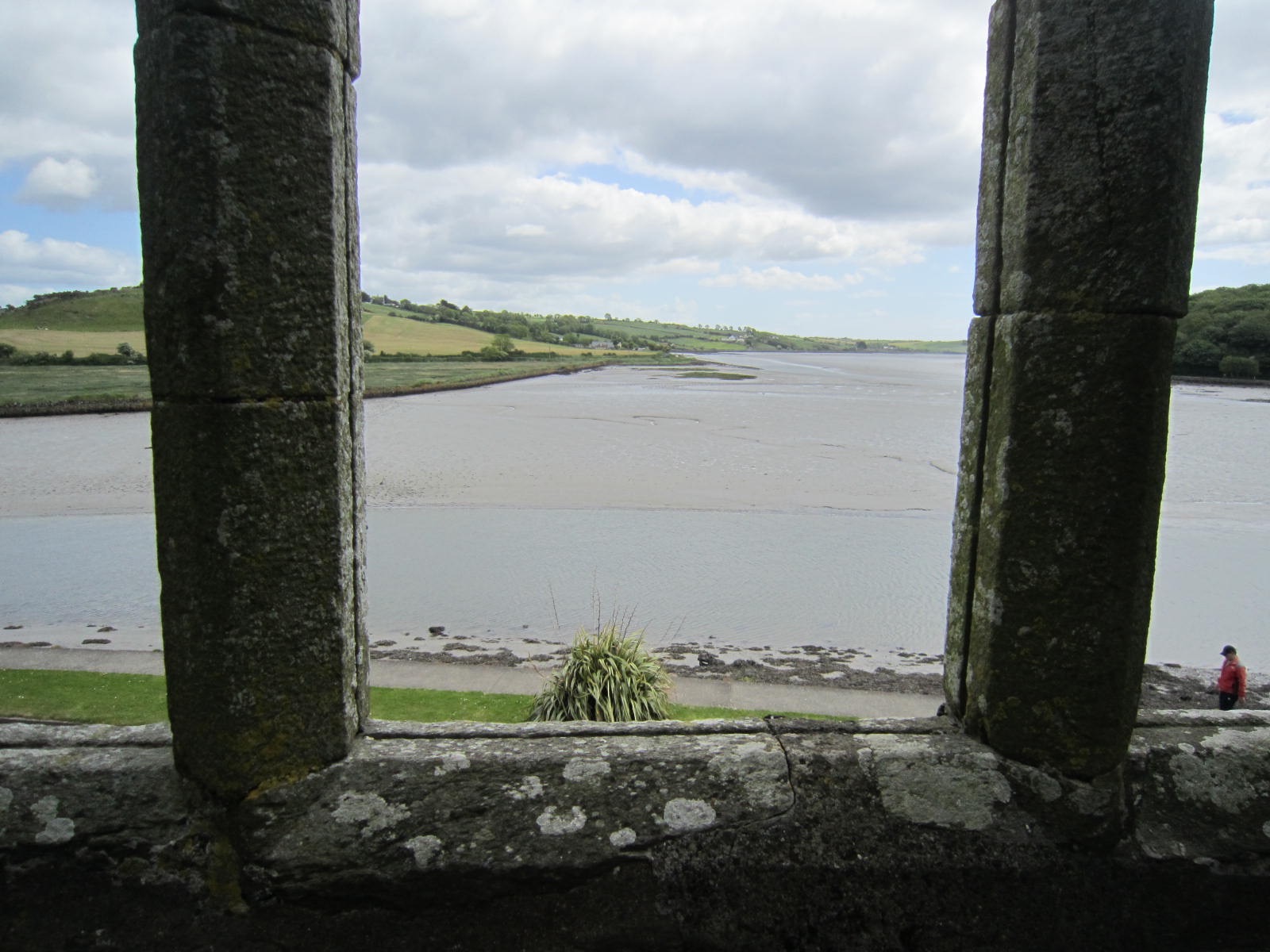
Timoleague is an Anglicization of the Irish Tigh Molaige, meaning House of Malaga for St. Malaga who is believed to have first brought beekeeping to Ireland. Foundation of the friary is attributed to the McCarthys in the 13th century, and also to William de Barry and his wife Margery de Courcy in the 14th century. Unfortunately, its position along the beautiful River Argideen and overlooking Courtmacsherry Bay made it vulnerable to Algerian pirates who sometimes cruised Ireland’s coastline in search of hostages and plunder.
 However, pirates may have seemed a minor threat compared the friary’s fate in the hands of the English. In King Henry VIII’s time, the structure was seized and as part of the Reformation the monks were dispersed. The monks returned in 1604, and then the English soldiers returned in 1612 to sack the buildings and smash all the stained glass windows. Then in 1642, English soldiers fighting the great Irish rebellion burned both the friary and town.
However, pirates may have seemed a minor threat compared the friary’s fate in the hands of the English. In King Henry VIII’s time, the structure was seized and as part of the Reformation the monks were dispersed. The monks returned in 1604, and then the English soldiers returned in 1612 to sack the buildings and smash all the stained glass windows. Then in 1642, English soldiers fighting the great Irish rebellion burned both the friary and town.
Many headstones dot the friary’s hillside, and large stone tombs in the nave are so ancient the chiseled inscriptions are no longer legible. Yet, the ruin is still an active cemetery for the local community.
Series posts:
Part 1 – Kanturk Castle Part 2 – Rock of Cashel
Part 3 – Barryscourt Part 4 – Ormonde Castle
Part 5 – Lismore Castle Part 6 - Bandon, Kilcolmen
 An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
The Prince of Glencurragh is available in ebook, soft cover and hard cover from online booksellers.
https://books2read.com/u/4N1Rj6
http://www.amazon.com/Prince-Glencurragh-Novel-Ireland-ebook/dp/B01GQPYQDY/
See all of my books and other information at
Part 6 in a series featuring sites I visited in Ireland while researching my second novel, The Prince of Glencurragh. See previous posts listed at the end.
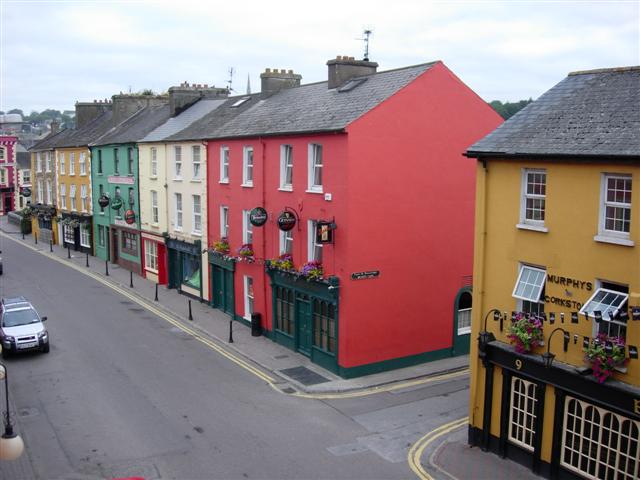

My research for The Prince of Glencurragh truly gained momentum when I visited Bandon in County Cork. Here I saw the place where my story began, and realized my reconnection with an old friend was the key that would allow the story to unfold.
Known as the gateway to West Cork, the city of Bandon lies 27 km (not quite 17 miles) west of Cork City. Established in 1604 as part of King James I’s Munster Plantation, it was a planned settlement English Protestants in Ireland. The famous stone bridge dates back at least to 1594, connecting people on either side of the Bandon River to facilitate trade. A timber bridge had existed even earlier, built by the O’Mahony (Oh-MAY-hon-ee) clan in 14th century.
When Richard Boyle, the first Earl of Cork, acquired the lease for all the properties of the town, he began a five-year project to enclose 27 acres within a wall nine feet thick and from 30 to 50 feet high in some places. On the heels of the Desmond Rebellions, this was intended to protect the peaceful settlers within against the wild Irish without.
Protection was needed against the unrest the settlement itself had created. Bandon lands had belonged to the O’Mahony and McCarthy clans, and the displacement left Irish families homeless and their sons without inheritance, sowing seeds for an even greater rebellion than the Desmonds could muster.
For the story in The Prince of Glencurragh, Bandon’s wall is critical, because certain local laws were enforced by a sheriff within the town’s walls, but did not extend beyond them. When the would-be “prince” Faolán Burke abducts his heiress from a rectory situated outside the town walls, technically he has broken no laws.
In preparation for my travels, my research uncovered a near-perfect model for this rectory, the Kilcolmen Rectory just east of where the walls of Bandon would have reached. To my surprise and delight, my dear friends and guides Eddie and Teresa actually live in Bandon (I had thought they still lived in Templemore).
I met Eddie when I was 19 or 20, visiting Ireland for a summer study program, and had the privilege of staying with his family in Skibbereen for a few days. We had not seen each other in decades, and so the reconnecting was gratifying and emotional.
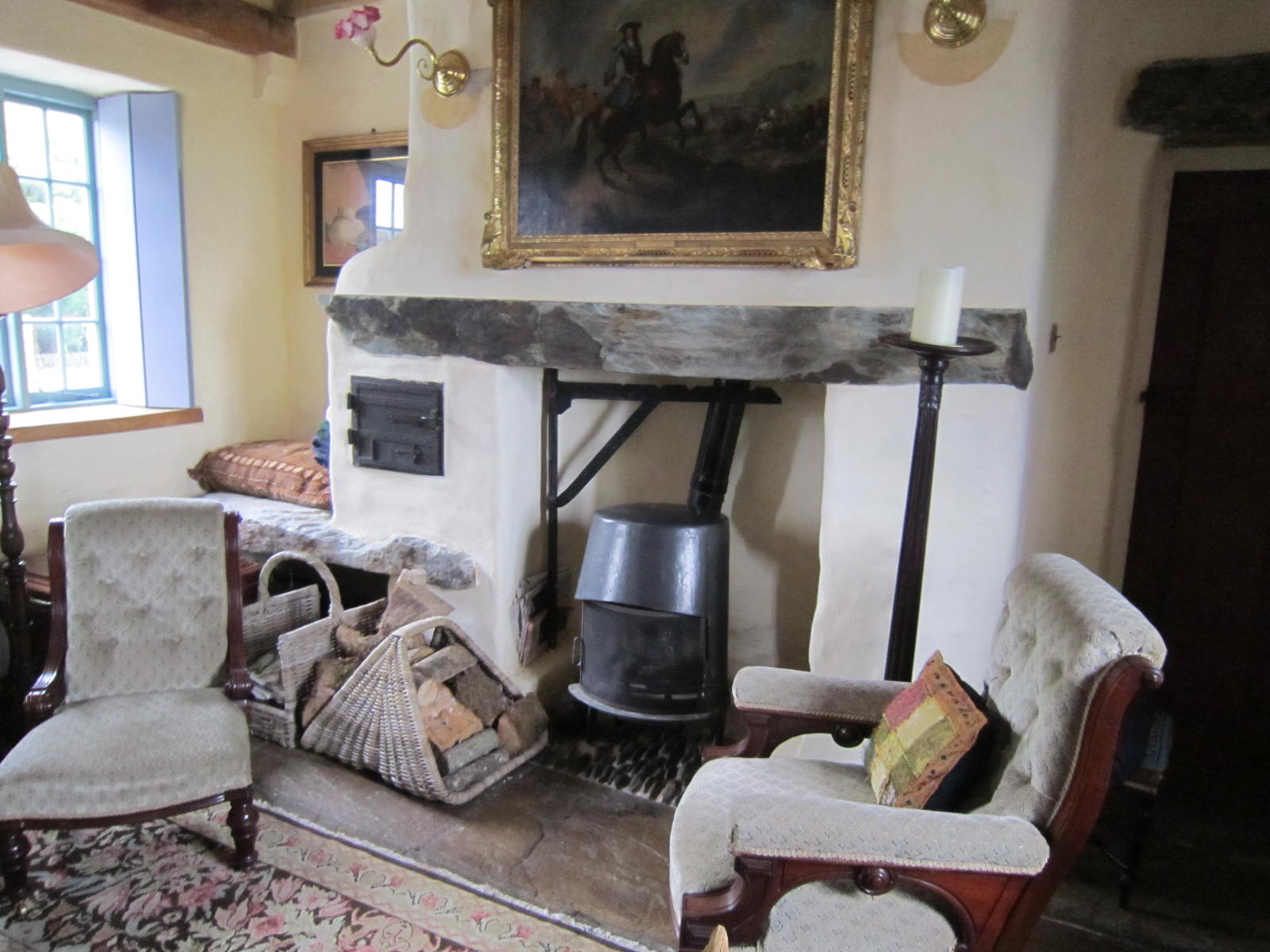
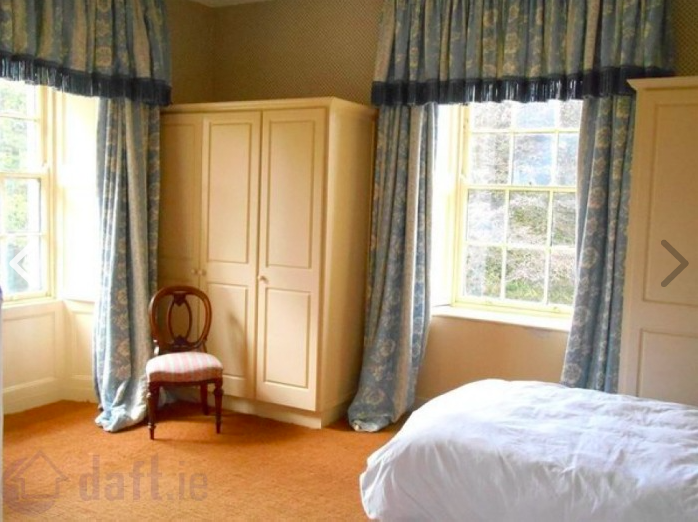
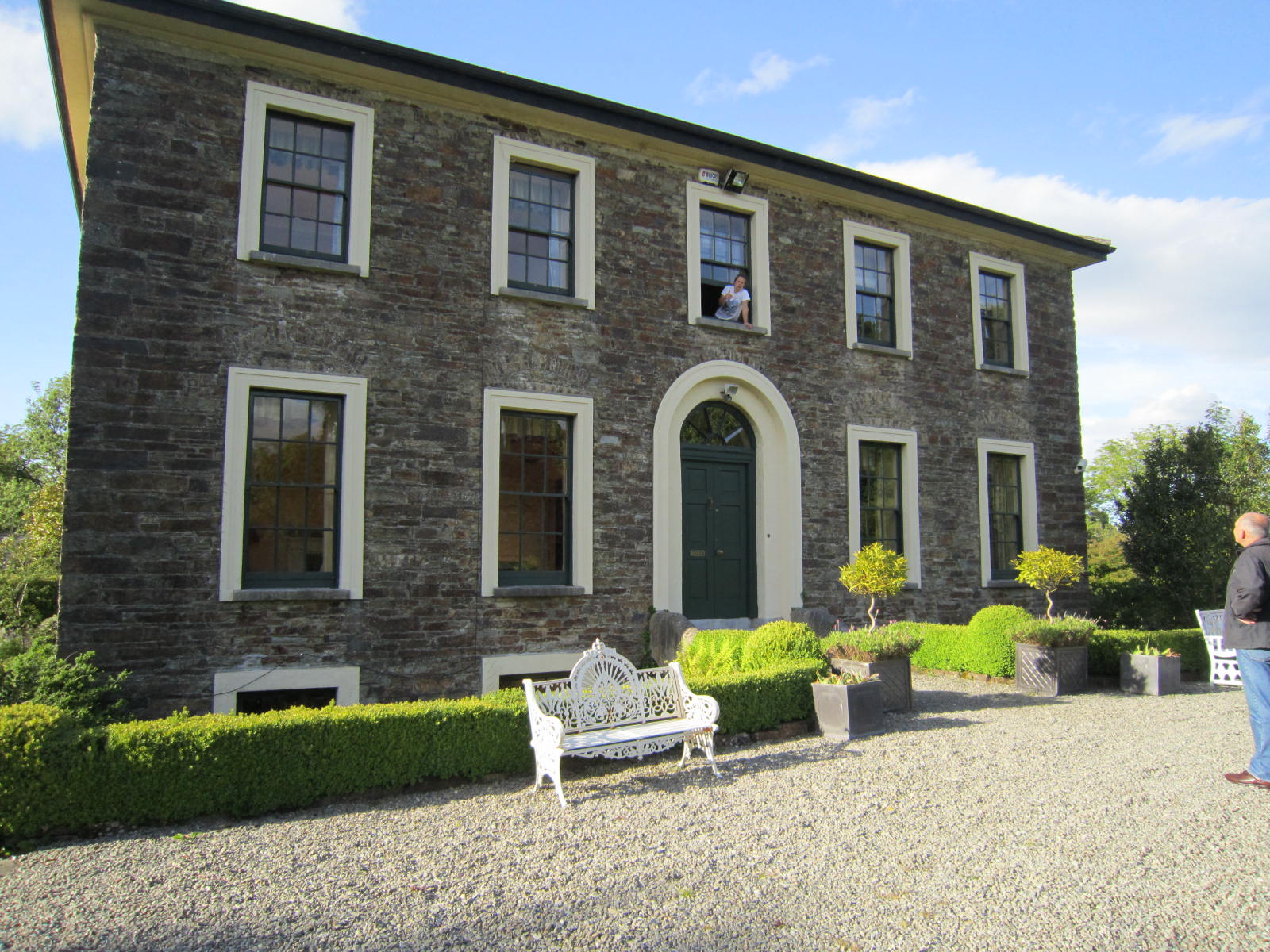 Eddie knew of the rectory and was able to take me straight there. Though it is now a private home, Eddie chatted with the resident—she was leaning out of the upstairs bathroom window where she’d been bathing her children—while I looked about the house and grounds. We did not go inside, but Eddie sent me some interior photos he happened upon when the house went on the real estate market months later.
Eddie knew of the rectory and was able to take me straight there. Though it is now a private home, Eddie chatted with the resident—she was leaning out of the upstairs bathroom window where she’d been bathing her children—while I looked about the house and grounds. We did not go inside, but Eddie sent me some interior photos he happened upon when the house went on the real estate market months later.
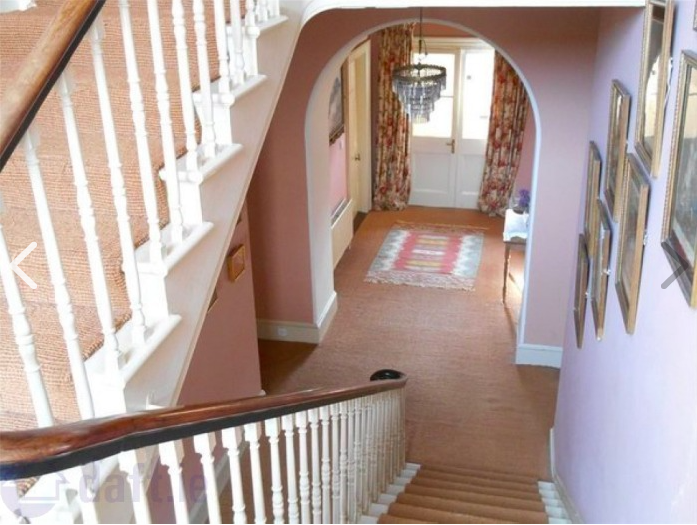 This rectory is much larger and finer than the one I had imagined, but served quite well to give me an authentic feel for the place. The front door is opposite the stairs, and on either side are doorways to the parlor and the dining room. I loved the enormous windows of the place, and the high ceilings. The bedroom is where the character Vivienne would have pushed her bed beneath a window to wait for St. Agnes to reveal the image of the man she would marry. The road outside would have been a dirt carriage path instead of a nice, clean paved drive.
This rectory is much larger and finer than the one I had imagined, but served quite well to give me an authentic feel for the place. The front door is opposite the stairs, and on either side are doorways to the parlor and the dining room. I loved the enormous windows of the place, and the high ceilings. The bedroom is where the character Vivienne would have pushed her bed beneath a window to wait for St. Agnes to reveal the image of the man she would marry. The road outside would have been a dirt carriage path instead of a nice, clean paved drive.
 Eddie later showed me that Bandon’s town walls are mostly invisible now but for some crumbling remnants. Still, the wall sets the town apart and Bandon is a member of the Irish Walled Towns Network.
Eddie later showed me that Bandon’s town walls are mostly invisible now but for some crumbling remnants. Still, the wall sets the town apart and Bandon is a member of the Irish Walled Towns Network.
Upon seeing these things, the story became real to me and I could tell it with sincerity. But the truth is I would never have found or seen the places I was looking for without Eddie and Teresa. It is one thing to look at a map and draw circles and lines, and yet another to actually find your way around a mostly unmarked and unfamiliar region. They took me everywhere I wanted to go, for they knew each place already, and even more than that, they had personal history with some of them, a love of exploration, and an often unspoken but clear reverence for the land and its history.
They showed me a ruin not on my list, but beautiful and fascinating: Castle Bernard. Where once there had been a medieval castle belonging to the O’Mahonys, in 1788 the first earl of Bandon, Francis Bernard, built a beautiful mansion with tall windows and soaring castellated towers.
By the time it was inhabited by the 4th earl, James Francis Bernard, a new and modern rising came from the IRA. In June 1921, while the earl hid in the cellar, IRA soldiers set fire to the castle and captured the earl as he tried to escape. Now mostly swallowed up by the woods and vines, the magnificence and inaccessibility of the ruin spur the imagination.
From Bandon we would travel for three spectacular days to uncover the rest of Faolán Burke’s trail.
As a side note, my friends in the Pacific Northwest might like to know that Bandon has a twin city agreement with Bandon, Oregon. In 1873, Lord George Bennet founded the city and named it after his hometown in Ireland. Bennet is known for introducing the lovely-flowering but highly troublesome gorse to the American landscape.
Thanks to: Irish Walled Town Network, Heritage Bridges of County Cork (Cork County Council), Castles.nl, Wikipedia and other sources.
Part 1 - Kanturk Castle
Part 2 - Rock of Cashel
Part 3 - Barryscourt
Part 4 - Ormonde Castle
Part 5 - Lismore Castle
 An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?The Prince of Glencurragh is available in ebook, soft cover and hard cover from online booksellers.
https://books2read.com/u/4N1Rj6
http://www.amazon.com/Prince-Glencurragh-Novel-Ireland-ebook/dp/B01GQPYQDY/
 On October 22, the Florida Writers Association bestowed the coveted Royal Palm Literary Award on my second novel, The Prince of Glencurragh. This is an enormous honor and a great thrill. I worked harder on this book than anything before, loved the story and characters, and I’m gratified that the judges loved it, too: first place for historical fiction, and first runner up for book of the year across all genres in its category.
So here’s the backstory: why I wrote it, what it’s about, and some themes that I hope will come through for readers.
On October 22, the Florida Writers Association bestowed the coveted Royal Palm Literary Award on my second novel, The Prince of Glencurragh. This is an enormous honor and a great thrill. I worked harder on this book than anything before, loved the story and characters, and I’m gratified that the judges loved it, too: first place for historical fiction, and first runner up for book of the year across all genres in its category.
So here’s the backstory: why I wrote it, what it’s about, and some themes that I hope will come through for readers.
This book is actually the prequel to my first novel, Sharavogue (also a Royal Palm award winner in 2014). It is about that protagonist’s father, Faolán Burke. I had originally intended to write the sequel, but at the time several readers urged me to tell what had happened before, and how Elvy Burke came to be in her troubled situation. So I focused instead on 1634, the year Elvy was born, and found the time rich with change, struggle, and growing discontent that would lead to the great Irish rebellion of 1641.
About the title
The Prince refers to the protagonist in the story, Faolán Burke, who aspires to be a leader among his people, and to build the castle that was his father’s dream. The gentleman on the cover is not a prince; he was James Butler, the 12th Earl of Ormonde, and later the first Duke of Ormonde, who embodied all the princely attributes of his day – he is the ideal, what Faolán would hope to become.
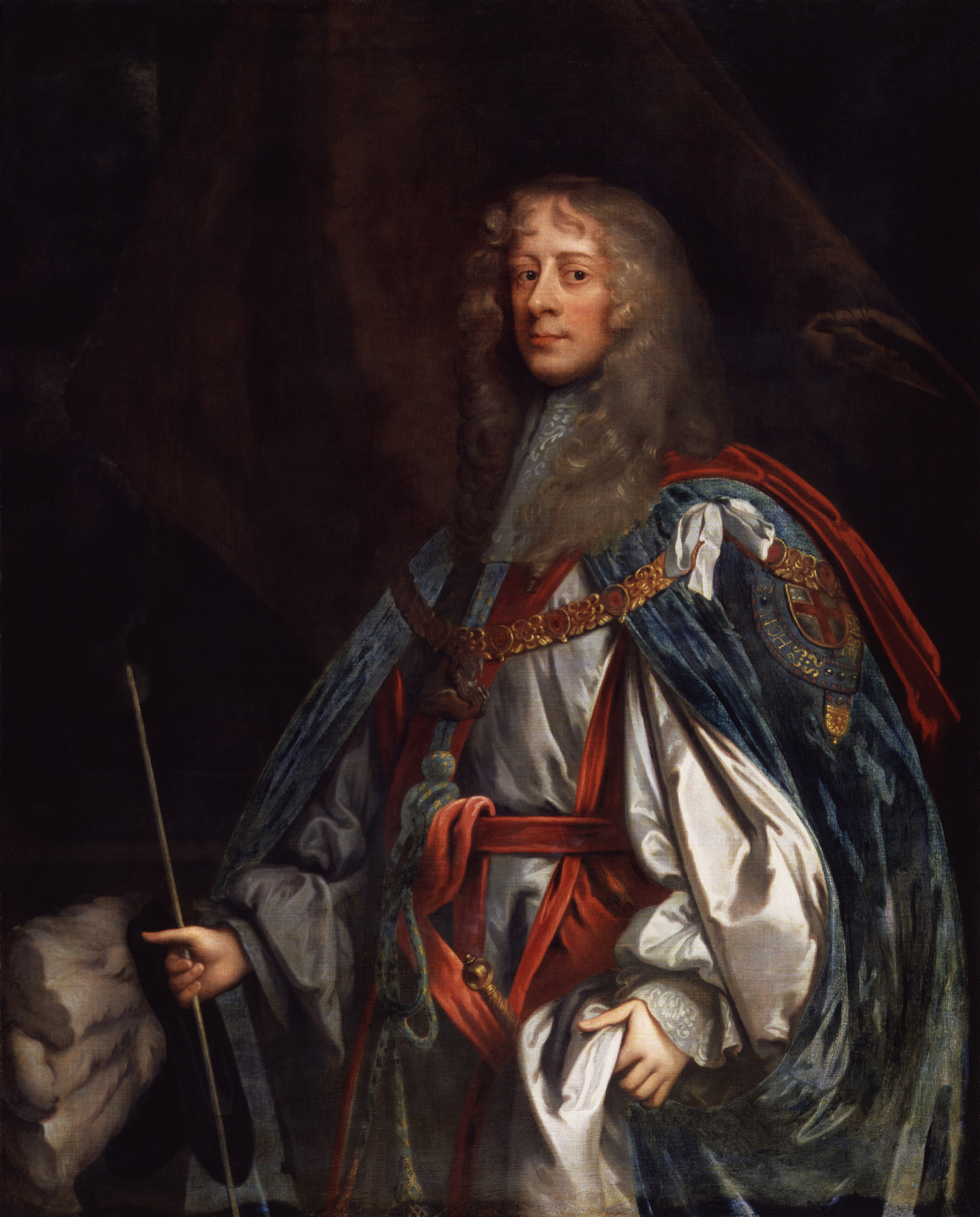

Ormonde was one of the largest landholders in Ireland at the time, and land was power. He ascended to the earldom at just 24 years of age, when his grandfather died, because the first heir, James’s father, had been lost at sea. This ceremonial portrait was a great inspiration to me: I was fascinated by the pride and strength in his face, the long golden curls, and the magnificent robes. He was admired by almost everyone in his day; he was a statesman of his time.
Biographer C.V. Wedgwood describes James Butler as a “high-hearted” nobleman: “Handsome, intelligent and valiant, he was also to the very core of his being a man of honor: loyal, chivalrous and just.”
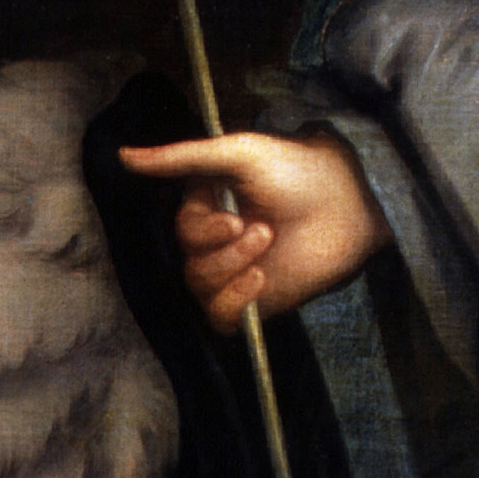 One little quirk you might notice on the cover, if you look at Ormonde’s right hand holding the lance. He appears to be missing a finger! In later portraits the finger exists, so this must be a mistake (or perhaps intentional) by the artist.
Glencurragh comes from a residential section of Skibbereen, a town in southwest County Cork (in the book I use the old spelling, Skebreen). When I visited there last year, my friend of many years helped me find the most likely place where my fictitious castle might have been located. Glencurragh means “a place for boats,” and the castle would’ve protected the commerce up and down the River Ilen. At one point in time there were three castles along the river at Skibbereen, but all have crumbled away.
One little quirk you might notice on the cover, if you look at Ormonde’s right hand holding the lance. He appears to be missing a finger! In later portraits the finger exists, so this must be a mistake (or perhaps intentional) by the artist.
Glencurragh comes from a residential section of Skibbereen, a town in southwest County Cork (in the book I use the old spelling, Skebreen). When I visited there last year, my friend of many years helped me find the most likely place where my fictitious castle might have been located. Glencurragh means “a place for boats,” and the castle would’ve protected the commerce up and down the River Ilen. At one point in time there were three castles along the river at Skibbereen, but all have crumbled away.
 It’s because of my affection for this friend and his family that both novels are set, at least in part, in their beautiful hometown, Skibbereen.
It’s because of my affection for this friend and his family that both novels are set, at least in part, in their beautiful hometown, Skibbereen.
So what’s the story about?
It’s about a young man chasing down a dream in the worst of times. Faolán Burke, son of a famous Irish warrior, is not a great catch. He should have inherited vast lands and the beautiful Castle Glencurragh. But the English lands confiscated the land, the castle of his father’s dreams was never built, and Faolán will try almost anything to make his lost heritage a reality.
In the opening scene, Faolán falls a bit short of his ideal. He’s abducting an heiress for his bride. There was no law against abduction at this time, and while I won’t say it was common, it did occur. Once abducted, women were considered soiled goods, the family could no longer negotiate a lucrative marriage settlement with a wealthy suitor, and usually would try to make the best of it with the family of the abductor.
In this case the heiress was under protection of an earl, and earls could generally exert their own law. So Faolán with his lady must run for cover until they have the protection and support of someone equal in power that can help negotiate the settlement.
But in 1634, the real world has changed. As the English plantation system spreads across the province of Munster, Irish families lose their homes to new English settlers. Lands that have been in their families for centuries now are given to English soldiers as rewards for service. Even castles, once both the bounty and protection of the strongest clans, now are vulnerable to the siege and cannon.
Moreover, knowledge and beliefs are changing. In the 17th century, Galileo and Newton founded modern science; Descartes began modern philosophy; Hobbes and John Locke started modern political theory. Science for the first time has greater influence than religion in decision-making. And people can own books. They become a symbol of wealth, and the bookshelf is invented to display them
Climatically, this was the middle of The Little Ice Age. The 1630s recorded great floods, widespread harvest failure, intense cold winters, wet and cold springs, and drought in summer.
Some scientists say even one degree of climate change can cause changes in human behavior. Faolán finds himself in the crossfire between the four most powerful—and irritable—men in Ireland, each with his own agenda.
THEMES:
Dreams: A young man trying to realize the dream of his father. Everyone has awakened from a dream so beautiful they want to hold onto it, but the longer they are awake the faster it recedes. From another perspective, many of us have seen the sacrifices our parents made and then tried to live their dream for them, only to realize later in life that it does not satisfy. We have to follow our own dreams.
Friendship: The relationship between best friends from childhood. Faolán interacts with his best friend Aengus O’Daly, who narrates the story. I am blessed to have known deep and lasting friendships of this kind that informed this story in ways I didn’t even realize until the end. I am truly grateful to my dear friends for that.
Hope. In great difficulty, when you have no power to change a circumstance that gives you pain, hope is what we rely on to get through, and it is the most human part of us.
Next: A Thorough Undoing
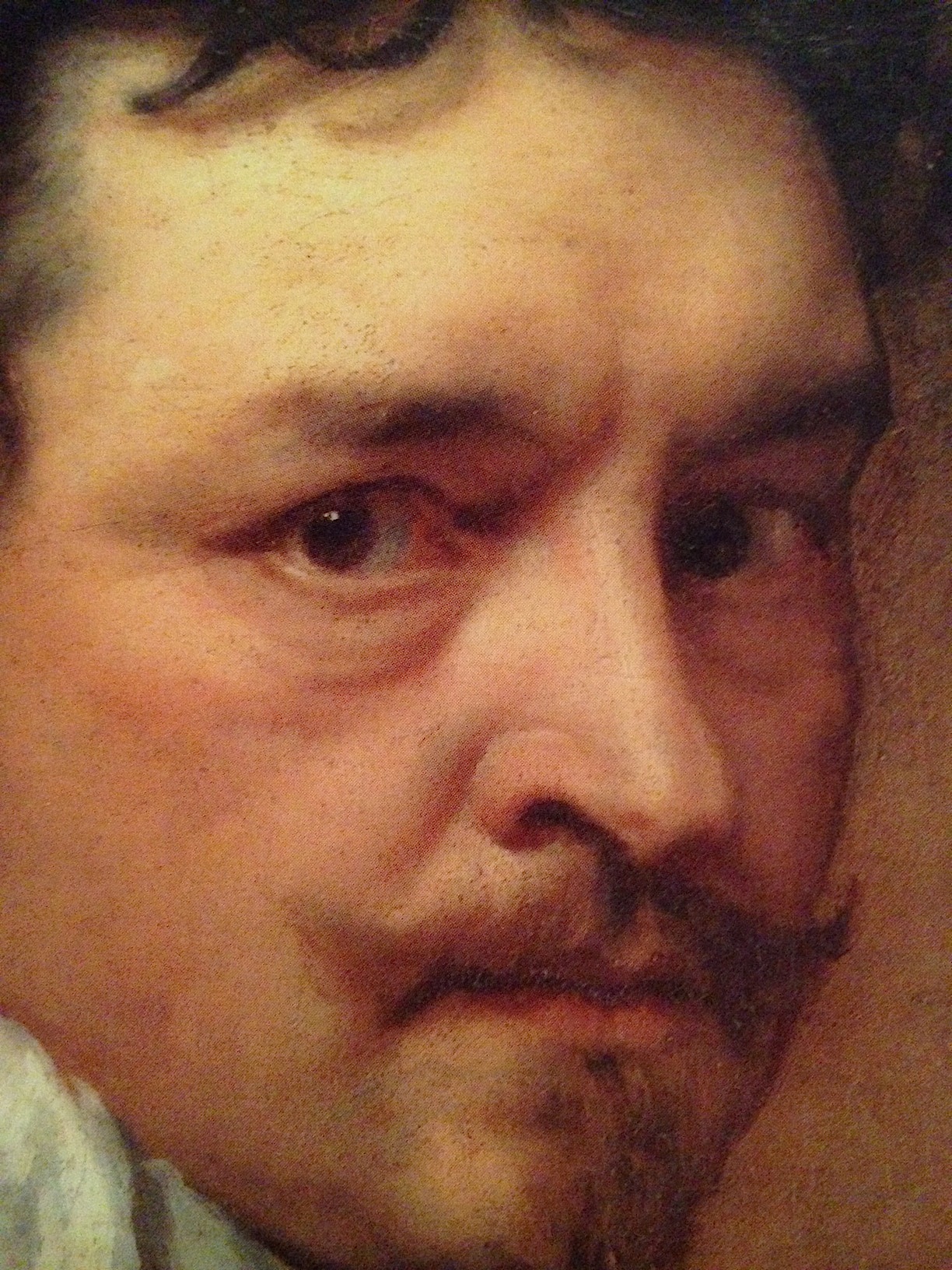 My next book picks up where this one ends, with events that occur between 1635 and 1641. Among English and Irish nobleman alike, hatred grows for the Lord Deputy of Ireland, Thomas Wentworth, and they set out to destroy him. In service of the Earl of Clanricarde, Faolán is charged to find the evidence that will strip Wentworth of his power.
My next book picks up where this one ends, with events that occur between 1635 and 1641. Among English and Irish nobleman alike, hatred grows for the Lord Deputy of Ireland, Thomas Wentworth, and they set out to destroy him. In service of the Earl of Clanricarde, Faolán is charged to find the evidence that will strip Wentworth of his power.
And now, a gentle request:
If you like what you read in The Prince of Glencurragh or any of my books, please take a moment to go online to Amazon, Goodreads, Barnes and Noble, or even Facebook, and write a quick review.
People buy books based on their friends’ recommendations, and book sales help authors pay for the editors, proofreaders and artists who help make the books the high quality you expect. Your words help authors with our words.
Thank you!
 An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
An heiress, a castle, a fortune: what could go wrong?
The Prince of Glencurragh is available in ebook, soft cover and hard cover from online booksellers.
https://books2read.com/u/4N1Rj6
http://www.amazon.com/Prince-Glencurragh-Novel-Ireland-ebook/dp/B01GQPYQDY/
See all of my books and other information at
Nancy Blanton is the award-winning author of Sharavogue, a historical novel set in 17th Century Ireland during the time of Oliver Cromwell, and in the West Indies, island of Montserrat, on Irish-owned sugar plantations. She has two more historical novels underway, as well as a non-fiction book about personal branding, Brand Yourself Royally in 8 Simple Steps. She also wrote and illustrated a children's book, The Curious Adventure of Roodle Jones, and co-authored Heaven on the Half Shell, the Story of the Pacific Northwest's Love Affair with the Oyster.

“Like reading The Three Musketeers for the first time!” —reader review of The Prince of Glencurragh